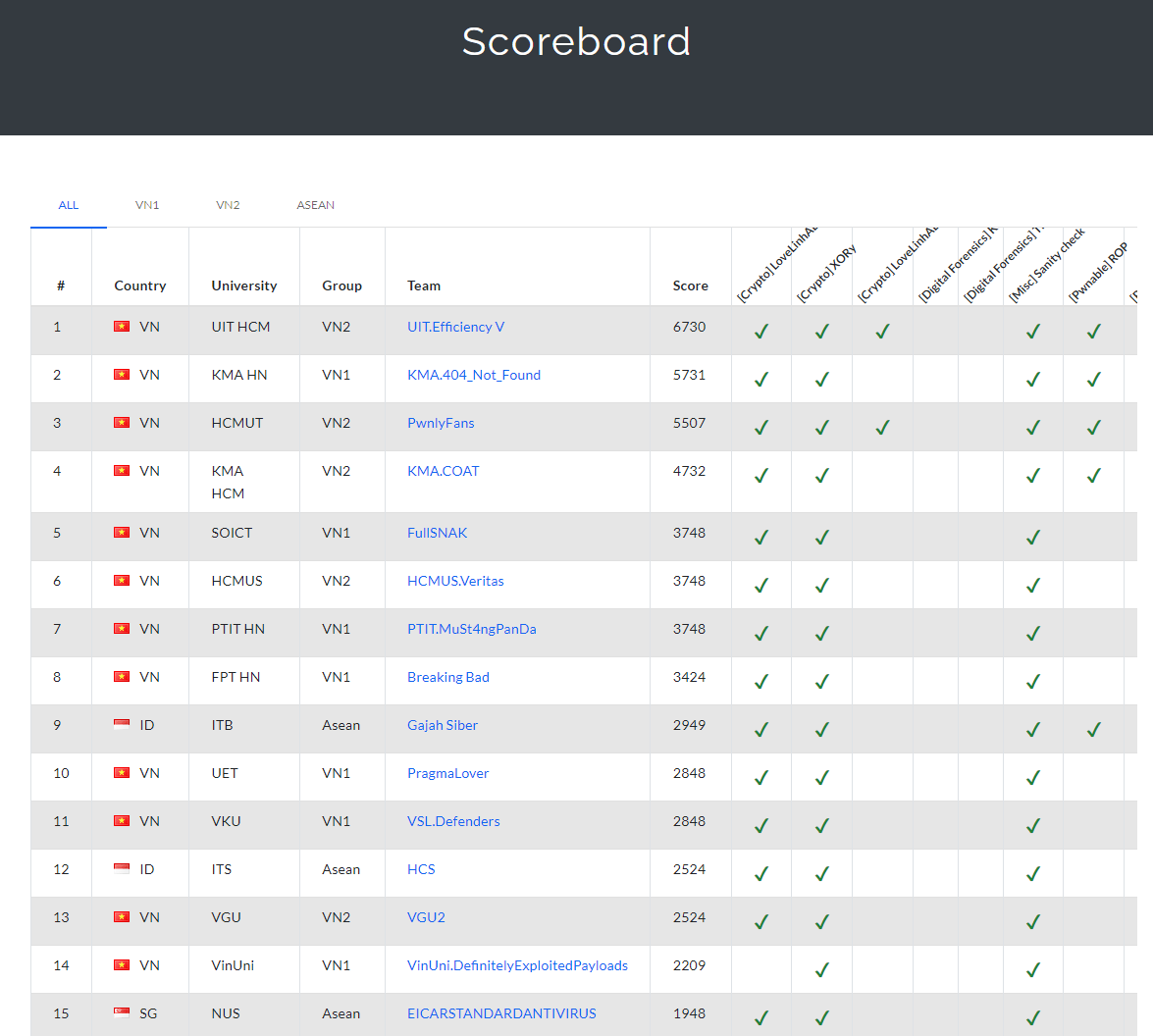
My team ‘Pwnlyfans’ recently participated in the ASCIS CTF 2024, and we managed to secure 3rd place and 2nd prize. This is a write-up for the crypto challenges we solved.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
import random, os
def xory(msg, key):
ct = []
for i in range(len(msg)):
ct.append(msg[i] ^ key[i%len(key)])
return bytes(ct)
#KEY = random.randbytes(5)
KEY = os.urandom(5)
FLAG = open('flag.txt', 'rb').read()
cipher = xory(FLAG, KEY)
print(cipher.hex())
|
We can see that it a easy stream cipher with the key length of 5 bytes. The flag format is ‘ASCIS{…}’. So from cipher we can get the key and decrypt the flag.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
from pwn import *
t = b'ASCIS'
def xory(msg, key):
ct = []
for i in range(len(msg)):
ct.append(msg[i] ^ key[i%len(key)])
return bytes(ct)
# io = remote('183.91.11.30',60001)
rec ='7db7c0aedc47bcb3b5d00dd1dc90bc088fdcd6e9639db392d0578ab390d06aafd69a85'
print(rec)
rec = bytes.fromhex(rec)
key = xor(t,rec[:5])
print(xor(key,rec[:5]))
msg = xory(rec,key)
print(msg)
#b'ASCIS{X0R_15_w34k_1f_y0u_kn0w_VKU}\n'
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
|
import random
import string
from Crypto.Util.number import isPrime
BLOCK_LEN = 129
CHARSET = string.ascii_uppercase + string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits
users, pwd_hashes = {}, []
allowed_blocks = []
q1 = 57895665874783536962369408363969823887021530656373208299565102620846005563716018275834077962292286213472570266375824572745671541793458387390711613089471407869558363212866932533545785125988453002675479793768261480181947144057144941974626043243654731721303589851520175899531854692118423229594279209070187162279
p1 = 2 * q1 + 1
g1 = 2
assert isPrime(p1)
assert isPrime(q1)
assert pow(g1, q1, p1) == 1
x1 = random.randint(1, 2 ** 256)
y1 = pow(g1, x1, p1)
def block_hash(block, bases, a):
for x, y in zip(bases, block):
a = a * pow(x, y, p1) % p1
return a
def secure_hash(data, token, is_login = False):
assert len(data) + 1 >= BLOCK_LEN, "Invalid Length"
if len(data) % BLOCK_LEN != 0:
data += b'\x80'
data += b'\x00' * (BLOCK_LEN - len(data) % BLOCK_LEN - 1)
blocks = [data[i:i + BLOCK_LEN] for i in range(0, len(data), BLOCK_LEN)]
bases = [pow(g1, x, p1) for x in token] + [g1]
yu_1 = y1
for block in blocks:
if is_login:
if block not in allowed_blocks:
print("Invalid block")
return False
yu_1 = block_hash(block, bases, yu_1)
allowed_blocks.append(block)
return yu_1
def register(username, password):
token = [random.randint(1, q1 - 1) for _ in range(BLOCK_LEN - 1)]
if username in users:
print("Username already exists")
return False
pwd_hash = secure_hash(password, token)
users[username] = token
pwd_hashes.append(pwd_hash)
return True
def login(username, password):
if username not in users:
return False
token = users[username]
try:
password.decode()
except:
return False
pwd_hash = secure_hash(password, token, True)
return pwd_hash in pwd_hashes
def breach(username):
if username not in users:
return None
return users[username]
def menu():
print("1. Register")
print("2. Login")
print("3. Exit")
def main():
admin_username = "admin"
admin_password = ''.join(random.choices(CHARSET, k = BLOCK_LEN - 1)).encode() + b'\x00'
register(admin_username, admin_password)
print(f'User {admin_username} registered successfully')
for _ in range(5):
try:
menu()
choice = int(input("> "))
except:
print("No No No No")
return
if choice == 1:
username = input("Enter username: ")
password = bytes.fromhex(input("Enter password: "))
if register(username, password):
print(f'User {username} registered successfully')
elif choice == 2:
username = input("Enter username: ")
password = bytes.fromhex(input("Enter password: "))
if login(username, password):
if username == admin_username:
print("Welcome admin, here is your flag: ")
print(open("flag.txt").read())
exit()
else:
print(f"Welcome user {username}")
else:
print("Invalid credential")
elif choice == 3:
print("Gud bye")
exit(0)
elif choice == 1337:
victim = input("Give me the victim name: ")
victim_token = breach(victim)
print("Shhhhh, don't tell anyone about this")
print(victim_token)
else:
print("Invalid choice")
exit(0)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
|
We encounter a custom hash function, when searching through the code I noticed that in the login fuction only check for the hash return from the secure_hash function is in the pwd_hashes list. So if we can craft a message that under the token for that ‘admin’ still in the list, we can login as admin and get the flag.
The step to solve this challenge is:
- Register a user ‘Malosdaf’ with a random password
- Using breach function to get the token of that admin and ‘Malosdaf’
- Recalculate the hash for ‘Malosdaf’.
- Digging deeper, we can see that the hash function is calulate by the following formula:
$$ y_{u_1} = g^{x_1} \times g^{tokenuser1 * block_1} \times g^{tokenuser2 * block_2} \times … \times g^{tokenusern* block_n} \mod p_1$$
So we can reduce the collision problem from multiplicatve group to the additive group by:
Assume the hash of ‘Malosdaf’ is $y_{u_1} = g^{target}$. The collision we must satisfy is:
$$ tokenuser[0] * b_1[0] + tokenuser[1] * b_1[1] + … + tokenuser[BLOCKSIZE-1] * b_1[BLOCKSIZE-1] $$ $$ = target \mod phi(q_1) \rightarrow \mod p_1 $$
Which the BLOCKSIZE is 129, The time complexity for naitive bruteforce is $O(2^{129})$ which is infeasible. So we will construct a matrix of size $BLOCKSIZE \times BLOCKSIZE$ and using LLL and CVP to solve the problem.
- Quicknote: This was my first thought when I saw the challenge, but I noticed that the login and resigter function isn’t checking for full 128 null bytes 🐧🐧 🤣. So we just create a random account which password is 128 null bytes and login again using admin with this password and get the flag.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
from pwn import *
# io = process(['python3','server.py'])
io = remote('183.91.11.30',5000)
io.sendlineafter('>',str(1))
io.sendlineafter(':',b'cc')
password = b'\x00'*128
io.sendlineafter(':',password.hex())
print(io.recvuntil('>'))
io.sendline(str(2))
io.sendlineafter(':',b'admin')
io.sendlineafter(':',password.hex())
io.interactive()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
|
import random
import string
from Crypto.Util.number import isPrime
BLOCK_LEN = 129
CHARSET = string.ascii_uppercase + string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits
users, pwd_hashes = {}, []
allowed_blocks = []
q1 = 57895665874783536962369408363969823887021530656373208299565102620846005563716018275834077962292286213472570266375824572745671541793458387390711613089471407869558363212866932533545785125988453002675479793768261480181947144057144941974626043243654731721303589851520175899531854692118423229594279209070187162279
p1 = 2 * q1 + 1
g1 = 2
assert isPrime(p1)
assert isPrime(q1)
assert pow(g1, q1, p1) == 1
x1 = random.randint(1, 2 ** 256)
y1 = pow(g1, x1, p1)
def block_hash(block, bases, a):
for x, y in zip(bases, block):
a = a * pow(x, y, p1) % p1
return a
def secure_hash(data, token, is_login = False):
assert len(data) + 1 >= BLOCK_LEN, "Invalid Length"
if len(data) % BLOCK_LEN != 0:
data += b'\x80'
data += b'\x00' * (BLOCK_LEN - len(data) % BLOCK_LEN - 1)
blocks = [data[i:i + BLOCK_LEN] for i in range(0, len(data), BLOCK_LEN)]
bases = [pow(g1, x, p1) for x in token] + [g1]
yu_1 = y1
for block in blocks:
if all(x == 0 for x in block[:-1]):
raise ValueError("No cheese this time")
if is_login:
if block not in allowed_blocks:
raise ValueError("Invalid block")
yu_1 = block_hash(block, bases, yu_1)
allowed_blocks.append(block)
return yu_1
def register(username, password):
token = [random.randint(1, q1 - 1) for _ in range(BLOCK_LEN - 1)]
if username in users:
print("Username already exists")
return False
pwd_hash = secure_hash(password, token)
users[username] = token
pwd_hashes.append(pwd_hash)
return True
def login(username, password):
if username not in users:
return False
token = users[username]
try:
password.decode()
except:
return False
pwd_hash = secure_hash(password, token, True)
return pwd_hash in pwd_hashes
def breach(username):
if username not in users:
return None
return users[username]
def menu():
print("1. Register")
print("2. Login")
print("3. Exit")
def main():
admin_username = "admin"
admin_password = ''.join(random.choices(CHARSET, k = BLOCK_LEN - 1)).encode() + b'\x00'
register(admin_username, admin_password)
print(f'User {admin_username} registered successfully')
for _ in range(5):
try:
menu()
choice = int(input("> "))
if choice == 1:
username = input("Enter username: ")
password = bytes.fromhex(input("Enter password: "))
if register(username, password):
print(f'User {username} registered successfully')
elif choice == 2:
username = input("Enter username: ")
password = bytes.fromhex(input("Enter password: "))
if login(username, password):
if username == admin_username:
print("Welcome admin, here is your flag: ")
print(open("flag.txt").read())
exit()
else:
print(f"Welcome user {username}")
else:
print("Invalid credential")
elif choice == 3:
print("Gud bye")
exit(0)
elif choice == 1337:
victim = input("Give me the victim name: ")
victim_token = breach(victim)
print("Shhhhh, don't tell anyone about this")
print(victim_token)
else:
print("Invalid choice")
exit(0)
except ValueError:
print("No No No No")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
|
This time author have fixed the previous bug, so we can’t use the same trick to get the flag. Back the the previous idea, we will contruct matrix to solve for the collision.
$$
\begin{pmatrix}
1 & 0 & 0 & \ldots & 0 & tokenuser[0] \
0 & 1 & 0 & \ldots & 0 & tokenuser[1] \
& & & \vdots & & & \
0 & 1 & 0 & \ldots & 1 & tokenuser[128] \
0 & 0 & 0 & \ldots & 0 & p_1 \
\end{pmatrix}
$$
And the target will vector will be:
$$ (tb[0],tb[1],tb[2], \ldots, tb[128], target) $$
while $t$ is the scaling factor. We can solve this problem using LLL and CVP. The rest of the code is struct construct the password and send it to the server.
- Note: The base is token + g1 so when construct the message we need to calculate for the difference between the target and the hash of the password.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
|
import os
os.environ['PWNLIB_NOTERM'] = '1'
os.environ['TERM'] = 'xterm-256color'
from pwn import *
import random
import string
from Crypto.Util.number import isPrime
from time import time
from sage.modules.free_module_integer import IntegerLattice
# Directly taken from rbtree's LLL repository
# From https://oddcoder.com/LOL-34c3/, https://hackmd.io/@hakatashi/B1OM7HFVI
def Babai_CVP(mat, target):
M = mat.LLL()
G = M.gram_schmidt()[0]
print('oke')
diff = target
for i in reversed(range(G.nrows())):
diff -= M[i] * ((diff * G[i]) / (G[i] * G[i])).round()
return target - diff
BLOCK_LEN = 129
CHARSET = string.ascii_uppercase + string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits
users, pwd_hashes = {}, []
allowed_blocks = []
q1 = 57895665874783536962369408363969823887021530656373208299565102620846005563716018275834077962292286213472570266375824572745671541793458387390711613089471407869558363212866932533545785125988453002675479793768261480181947144057144941974626043243654731721303589851520175899531854692118423229594279209070187162279
p1 = 2 * q1 + 1
g1 = 2
assert isPrime(p1)
assert isPrime(q1)
assert pow(g1, q1, p1) == 1
y1 = int(0)
def block_hash(block, bases, a):
for x, y in zip(bases, block):
a = a * pow(x, y, p1) % p1
return a
def mod_block_hash(block,bases,a):
for x,y in zip(bases,block):
a = (a + (x*y))%q1
return a
def secure_hash(data, token):
assert len(data) + 1 >= BLOCK_LEN, "Invalid Length"
if len(data) % BLOCK_LEN != 0:
data += b'\x80'
data += b'\x00' * (BLOCK_LEN - len(data) % BLOCK_LEN - 1)
blocks = [data[i:i + BLOCK_LEN] for i in range(0, len(data), BLOCK_LEN)]
bases = token + [1]
yu_1 = y1
for block in blocks:
yu_1 = mod_block_hash(block, bases, yu_1)
allowed_blocks.append(block)
return yu_1
start = time()
io = process(['python3','server.py'])
# io = remote('183.91.11.30',666)
io.recvuntil('>')
io.sendline(str(1337))
io.sendlineafter('Give me the victim name:',b'admin')
io.recvuntil('this')
token_admin = io.recvuntil(']').strip()
token_admin = eval(token_admin)
print(len(token_admin))
#print(token_admin)
io.sendlineafter('>',str(1))
io.recvuntil(':')
io.sendline(b'a')
password_a = b'z'*128 + b'\x00'
io.recvuntil(':')
io.sendline(password_a.hex())
io.recvuntil('>')
io.sendline(str(1337))
io.sendlineafter('Give me the victim name:',b'a')
io.recvuntil('this')
token_a = io.recvuntil(']').strip()
token_a = eval(token_a)
target = secure_hash(password_a,token_a)
target = target%q1
b = []
for i in range(BLOCK_LEN-1):
vec = [0 for i in range(BLOCK_LEN)]
vec[-1] = token_admin[i]
vec[i] = 1
b.append(vec)
vec = [0 for i in range(BLOCK_LEN)]
vec[-1] = q1
b.append(vec)
b = matrix(ZZ,b)
t = 2^10
while t<=2^15:
up = [t]*(128) + [target]
result = Babai_CVP(b,vector(ZZ,up))
print(result)
x = min(result)
t*=2
if x >= 0:
print(target-result[-1])
if target-result[-1] >= 0:
print('pass')
break
diff = target - result[-1]
result = result[:-1]
print(diff)
a = []
while max(result) > int(0):
s=b''
for i in range(len(result)):
if result[i]>int(127):
s+=bytes([int(127)])
result[i]-=int(127)
else:
s+=bytes([result[i]])
result[i]=0
if diff>int(127):
s+=bytes([int(127)])
diff-=int(127)
else:
s+=bytes([diff])
diff=0
a.append(s)
oo = b''.join(a)
io.sendlineafter('>',str(1))
io.sendlineafter(':',b'cc')
io.sendlineafter(':',oo.hex())
print(io.recvuntil('>'))
io.sendline(str(2))
io.sendlineafter(':',b'admin')
io.sendlineafter(':',oo.hex())
end = time()
print('Time = ',end-start)
io.interactive()
|
This solution is quite slow because LLL on matrix size 129x129 but still far better than $O(2^{129})$. We can further improve by using flatter.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
def flatter(M):
# compile https://github.com/keeganryan/flatter and put it in $PATH
# if flatter is not available we can just return M.LLL() instead
from subprocess import check_output
from re import findall
z = "[[" + "]\n[".join(" ".join(map(str, row)) for row in M) + "]]"
ret = check_output(["flatter"], input=z.encode())
return matrix(M.nrows(), M.ncols(), map(ZZ, findall(b"-?\\d+", ret)))
# Directly taken from rbtree's LLL repository
# From https://oddcoder.com/LOL-34c3/, https://hackmd.io/@hakatashi/B1OM7HFVI
def Babai_CVP(mat, target):
M = flatter(mat)
G = M.gram_schmidt()[0]
print('oke')
diff = target
for i in reversed(range(G.nrows())):
diff -= M[i] * ((diff * G[i]) / (G[i] * G[i])).round()
return target - diff
|
Which usually reduce the time. This is the comparison between the two code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
Time = 149.55928230285645
[*] Switching to interactive mode
Welcome admin, here is your flag:
Malosdaf
[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
Time = 56.560893058776855
[*] Switching to interactive mode
Welcome admin, here is your flag:
Malosdaf
[*] Got EOF while reading in interactive
|
